July 7, 2023
In the realm of energy production, gaining a clear understanding of the actual expenses associated with generating electricity is crucial. The Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) is a simple yet powerful tool that helps us compare the costs of different energy sources. It considers the upfront investment, operating expenses, and lifespan of a power plant to determine the average cost of producing electricity over time. This article aims to explain LCOE in simple terms with a straightforward example.
LCOE consists of the net present value of the unit cost of electricity over the lifetime of a system:
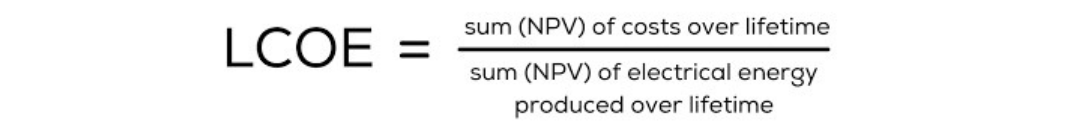
The Calculation Process:
To delve into calculations of LCOE, we require three fundamental pieces of information:
-
Capital Costs: the upfront investment required to construct the power plant, including equipment, infrastructure, and installation.
-
Operating Costs: the ongoing expenses for operating and maintaining the plant – labor, fuel, maintenance, and repairs.
-
Lifetime Electricity Generation: the total amount of electricity anticipated to be generated by the plant throughout its operational lifetime.
After gathering the necessary information, typically provided by future construction companies or turnkey solution providers like Sunwise, the calculation process can commence. Here’s an example illustrating, how LCOE works in the Latvian market with Altum support.
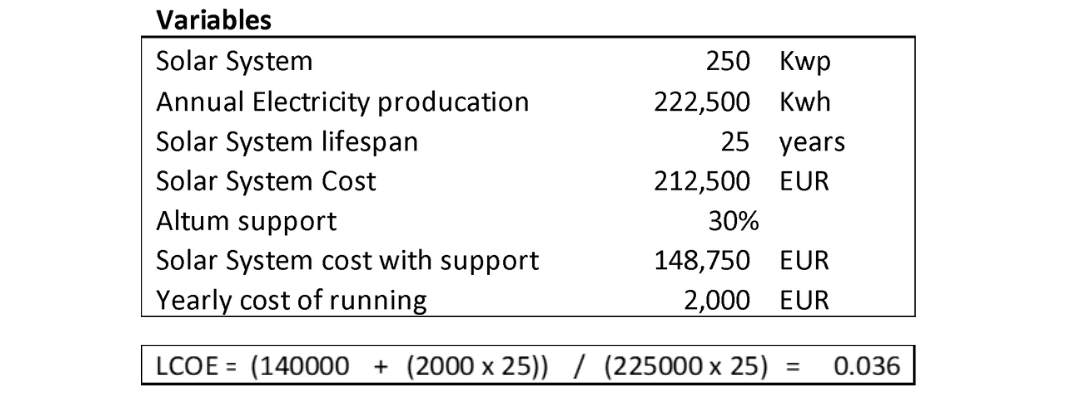
Understanding the Results:
Upon obtaining the LCOE results, it is essential to grasp their significance. For instance, if the calculated LCOE value is 0.036, it signifies that by implementing a solar energy generating system on your property, you can anticipate receiving approximately 22 GWh of electricity per year for the next 25 years for 0.034 EUR per unit.
Other things to consider when assessing the true cost of power generation:
1) Environmental Impact: traditional fossil fuel-based power plants contribute to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, which can have detrimental effects on climate change and human health. Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind offer cleaner alternatives with lower environmental impacts.
2) Grid Integration and Infrastructure: upgrading and expanding the grid infrastructure may be necessary to accommodate renewable energy projects, adding to the overall costs. But by generating electricity on-site, individuals and businesses can reduce reliance on external power grids and mitigate the impact of rising energy costs. Thus the investment on average pays off in 4-7 years, while the system lifespan is 30 years.
3) Technological Advancements and Innovation: the rapid pace of technological advancements in the energy sector can significantly lower the cost of power generation. Solar technology has experienced significant advancements, resulting in improved efficiency and affordability. The declining costs of solar panels, coupled with favorable government incentives and financing options, make solar energy an increasingly attractive and financially viable choice.
4) Policy and Regulatory Framework: incentives, subsidies, and regulations that promote renewable energy adoption can make clean energy sources more economically viable. Conversely, policies that support or penalize specific energy sources can influence the overall cost competitiveness of different technologies. However, in the long run, now we need to take into consideration that at the EU scale all countries not implementing CO2 reduction incentives by 2030, will be penalised and in this case, companies will be the ones who will need to pay these fines in forms of higher taxes or cost of electricity.
5) Socioeconomic Factors: it’s important to consider the broader socioeconomic impacts of power generation methods. For example, the deployment of renewable energy projects can create jobs, stimulate local economies, get green certificates to companies and their ratings for bank loans or international listings, and enhance energy independence.
Conclusion:
The Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) is an invaluable tool for comparing the costs associated with different energy sources. By taking into account the upfront investment, operating expenses, and lifetime electricity generation, LCOE provides a fair assessment of the true cost of power generation. When assessing the true cost of power generation, solar energy emerges as a compelling choice. With lower operating costs, long lifespan, environmental benefits, and technological advancements, solar energy offers a cost-effective, sustainable, and socially responsible solution.
Take the next step towards unlocking the full potential of your future or existing system. Schedule a meeting with us now, and let’s explore the possibilities for your commercial property together. Email: info@sunwise.lv
